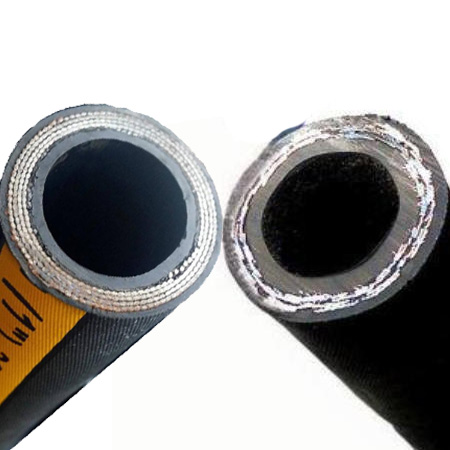
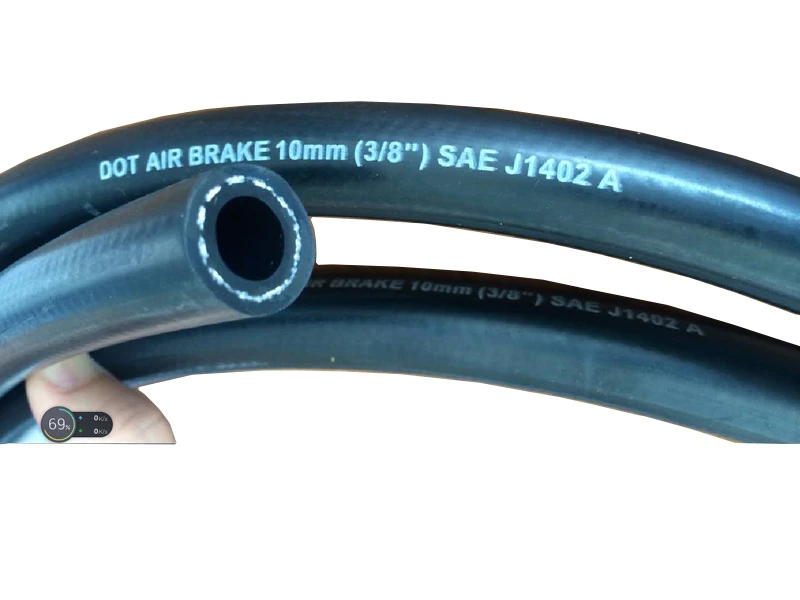
High pressure hoses are critical components in various industrial, automotive, and hydraulic systems. Designed to withstand extreme pressures, these hoses ensure the safe and efficient transfer of fluids, gases, and chemicals.
First of all,
high pressure hoses
are categorized based on their construction and material composition. The
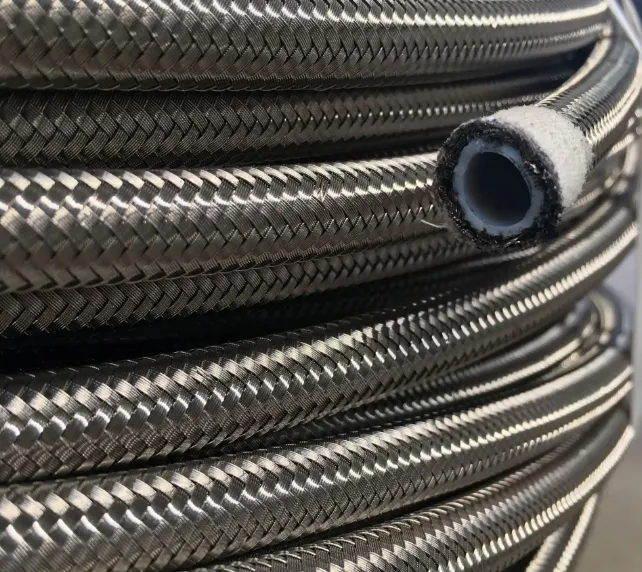
In addition, PTFE braided hose represents a specialized category designed for handling highly corrosive fluids and gases. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) liners provide near-universal chemical compatibility, while stainless steel braiding enhances structural integrity. The braided PTFE fuel hose is a specific subtype optimized for fuel transfer applications, featuring additional barriers to prevent permeation and static buildup in automotive and aerospace systems.
Besides, high-temperature applications require specialized solutions such as the high temp braided hose , such as high temperature SAE 1005, These hoses incorporate heat-resistant materials like silicone or fluoropolymer liners, combined with high-grade metal braiding to maintain performance in environments exceeding 275°F. The braided power steering hose demonstrates another application-specific design, featuring multiple reinforcement layers to withstand the pulsating pressures and constant flexing in vehicle steering systems while resisting oil degradation.
High pressure hoses
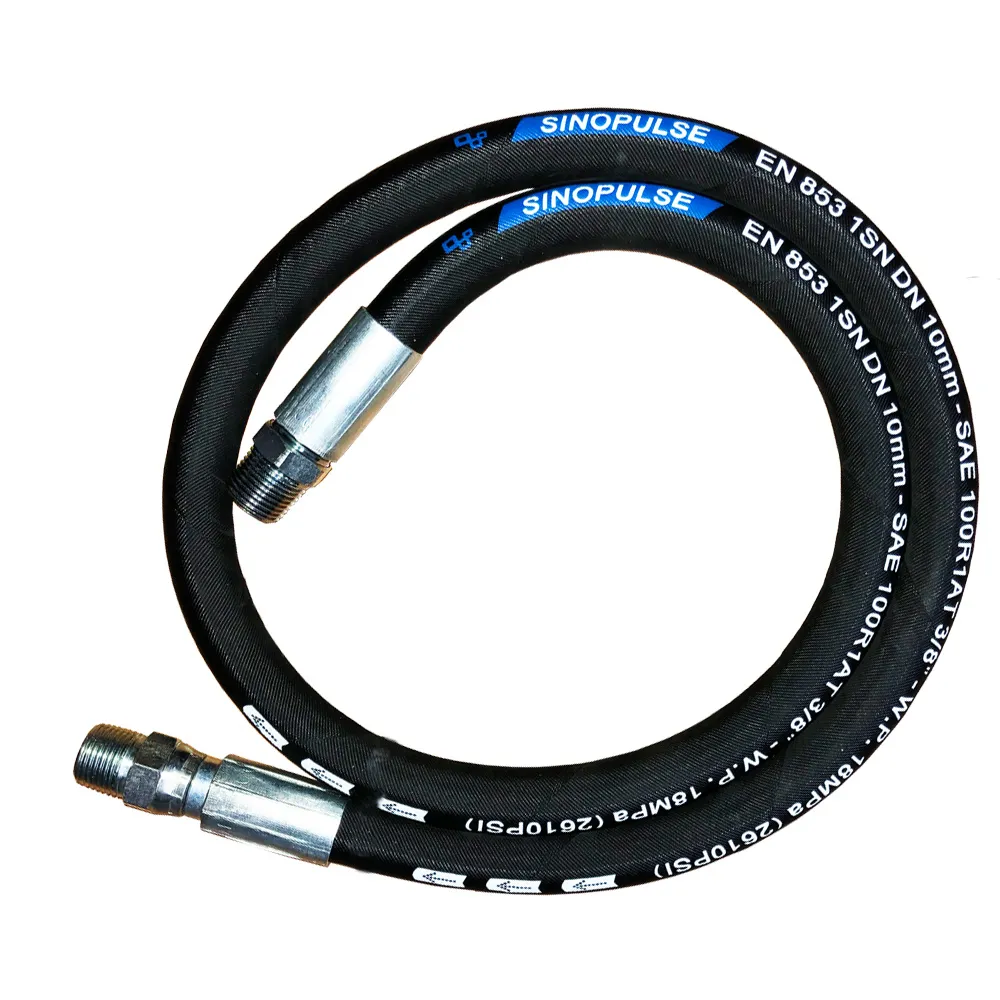
serve a broad range of industries due to their adaptability and strength. Hydraulic systems across multiple sectors rely heavily on hoses meeting
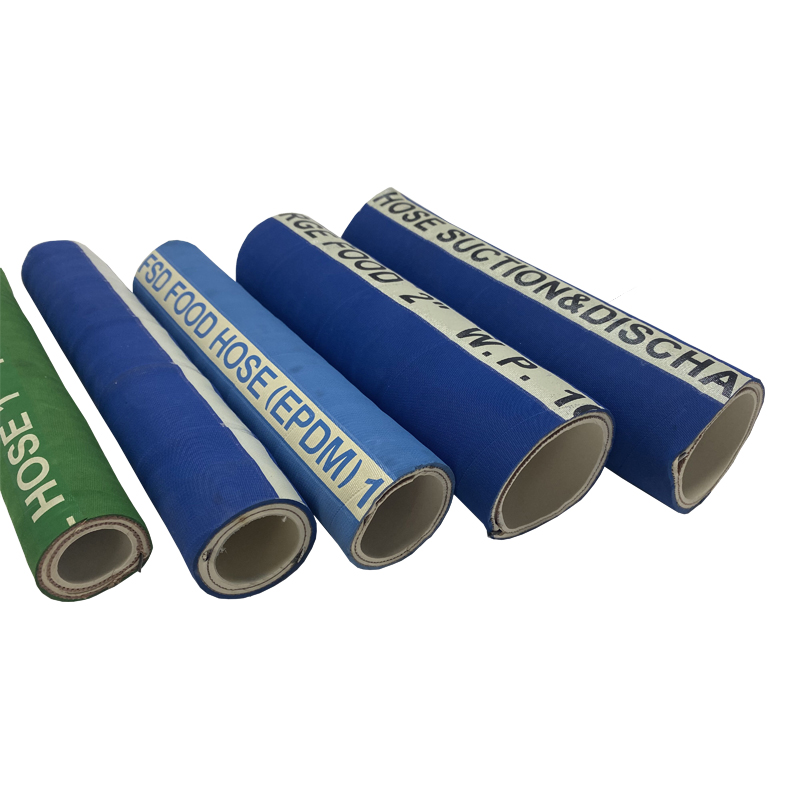
Furthermore, the high pressure thermoplastic hose finds extensive use in chemical processing plants. Its unique material composition allows for safe transfer of aggressive media including concentrated acids, caustic solutions, and hydrocarbon mixtures. These hoses often feature color-coded exteriors for easy identification of their chemical compatibility range in complex industrial environments.
Last, in automotive engineering, specialized hoses like the braided PTFE fuel hose play critical roles in vehicle functionality. Modern fuel systems demand hoses that can withstand ethanol-blended fuels while meeting strict emissions standards, while power steering systems require hoses capable of maintaining seal integrity despite constant pressure fluctuations and vibration exposure.
First of all, regular inspection is crucial to prevent hose failure. Technicians should examine hoses for signs of external damage including cuts, abrasions, or kinking that may compromise structural integrity. Internal degradation can be detected through fluid contamination analysis or unexpected pressure drops in the system. Proper storage conditions involve keeping hoses coiled loosely in climate-controlled environments away from ozone sources and direct sunlight.
In addition, proper hose selection requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Pressure ratings must exceed maximum system pressures by an appropriate safety margin, while temperature ranges should account for both operational heat and ambient conditions. Chemical compatibility charts should be consulted when selecting a
Finally, installation practices significantly impact hose service life. Proper routing prevents unnecessary bending or torsion stresses, while adequate support spacing minimizes vibration-induced wear. Adherence to manufacturer-specified torque values during fitting assembly ensures leak-free connections without damaging hose ends. Periodic replacement intervals, even for apparently undamaged hoses, should follow industry-recommended schedules particularly for safety-critical applications.
The proper selection, application, and maintenance of high pressure hoses directly impact operational efficiency and workplace safety across numerous industries. As demonstrated throughout this guide, each hose variant – from thermoplastic high pressure hose to specialized SAE 100R 1 4 compliant models – serves distinct purposes under specific operating conditions. The PTFE braided hose and braided PTFE fuel hose exemplify how material science advancements address challenging chemical transfer requirements, while high temp braided hose solutions showcase engineering adaptations for extreme thermal and mechanical stresses.
Effective hose maintenance requires regular inspections, testing, and timely replacements. Proper staff training in installation and defect recognition prevents failures and downtime. With increasing industrial demands for extreme pressures and harsh media, ongoing high pressure hose innovation is vital for safety and performance. Following these guidelines enables optimal system reliability while reducing operational risks.