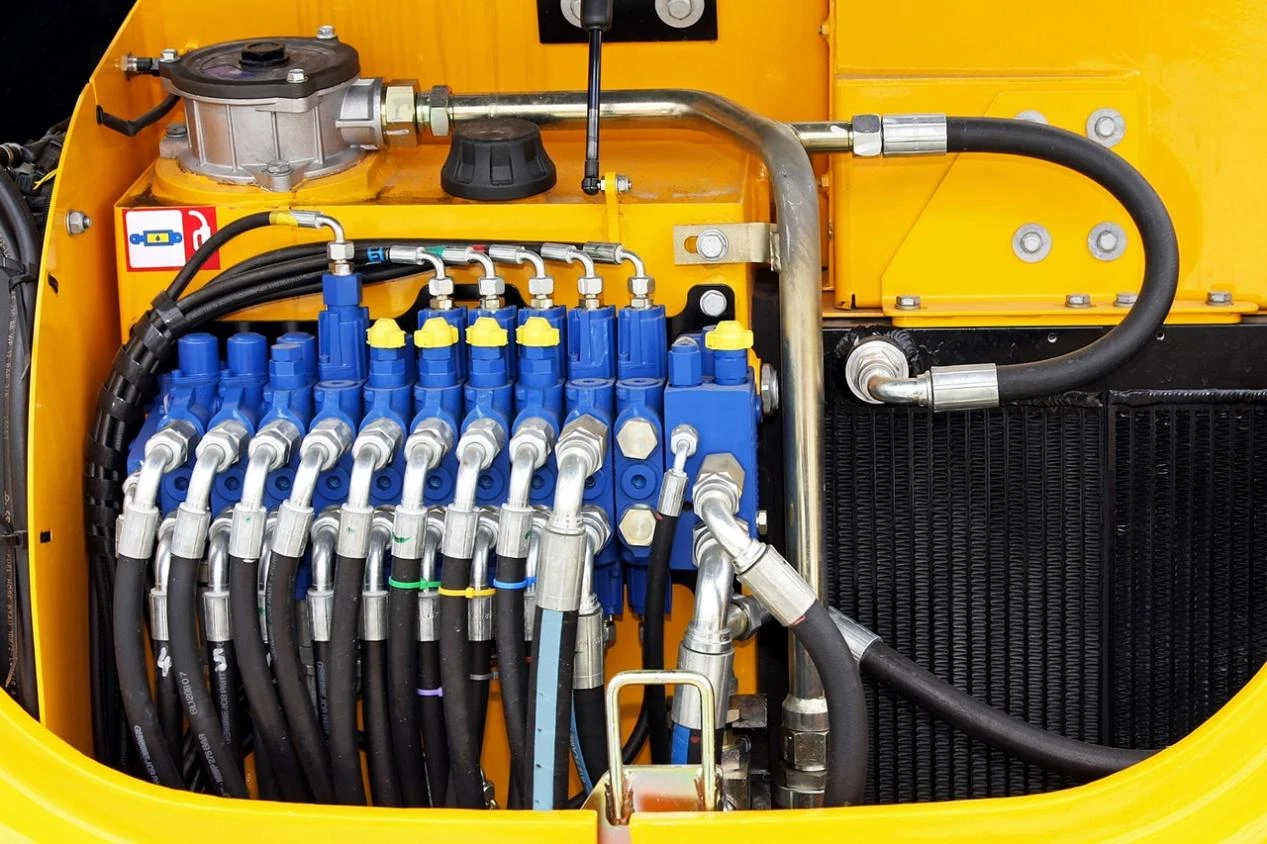
In the intricate web of industrial fluid transfer, the choice between silicone hoses and rubber hoses can make or break operational efficiency. As a trusted rubber hose manufacturer , SINOPULSE understands that selecting the right hose hinges on understanding its unique properties, strengths, and ideal applications. This guide unravels the distinctions between these two essential components, empowering you to choose with confidence, whether for high-pressure hydraulics, chemical handling, or food-grade environments.
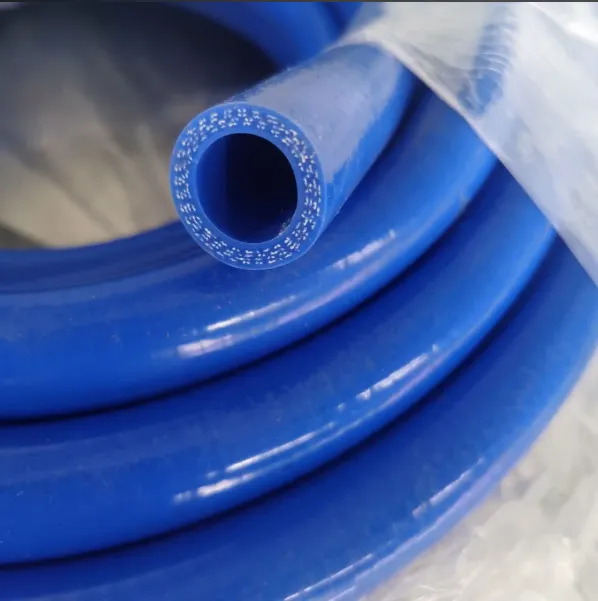

Silicone hoses are crafted from silicone rubber, a synthetic polymer celebrated for its exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness. Unlike traditional rubber, silicone thrives in extreme temperature ranges, withstanding -60°C to 200°C (and up to 300°C in specialized formulations) without losing flexibility. This makes them indispensable in scenarios where heat or cold would degrade other materials.
Key characteristics of silicone hoses include:
- Food-Grade Compliance : Smooth, non-toxic inner surfaces meet FDA and EU 10/2011 standards, making them ideal for food and beverage processing, where contamination risks are zero-tolerance.
- Chemical Neutrality : Resistant to water, steam, and mild acids, though less suited for harsh solvents or oils.
- Low Compression Set : Maintains elasticity even after prolonged use, critical for sealing applications in medical equipment or pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Their limitations? Silicone lacks the abrasion resistance and high-pressure tolerance of rubber, making it less suitable for heavy-duty industrial tasks like hydraulic systems or fuel transfer.
Rubber hoses—particularly
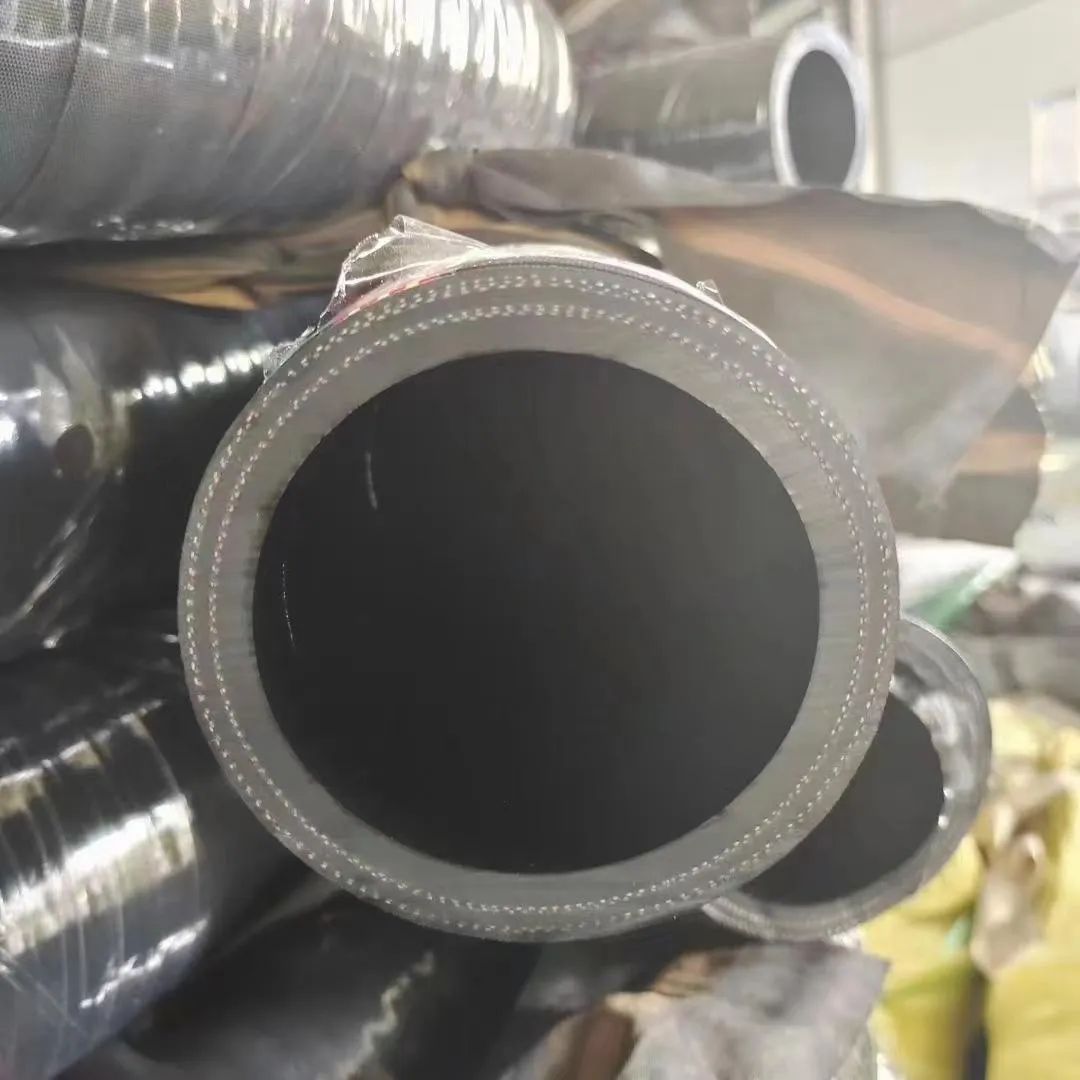

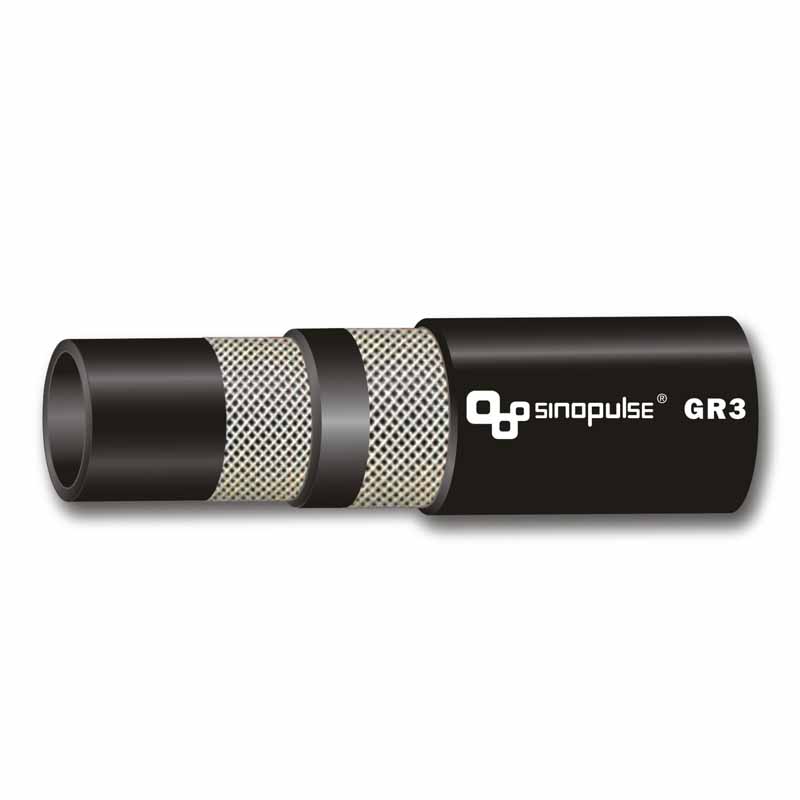
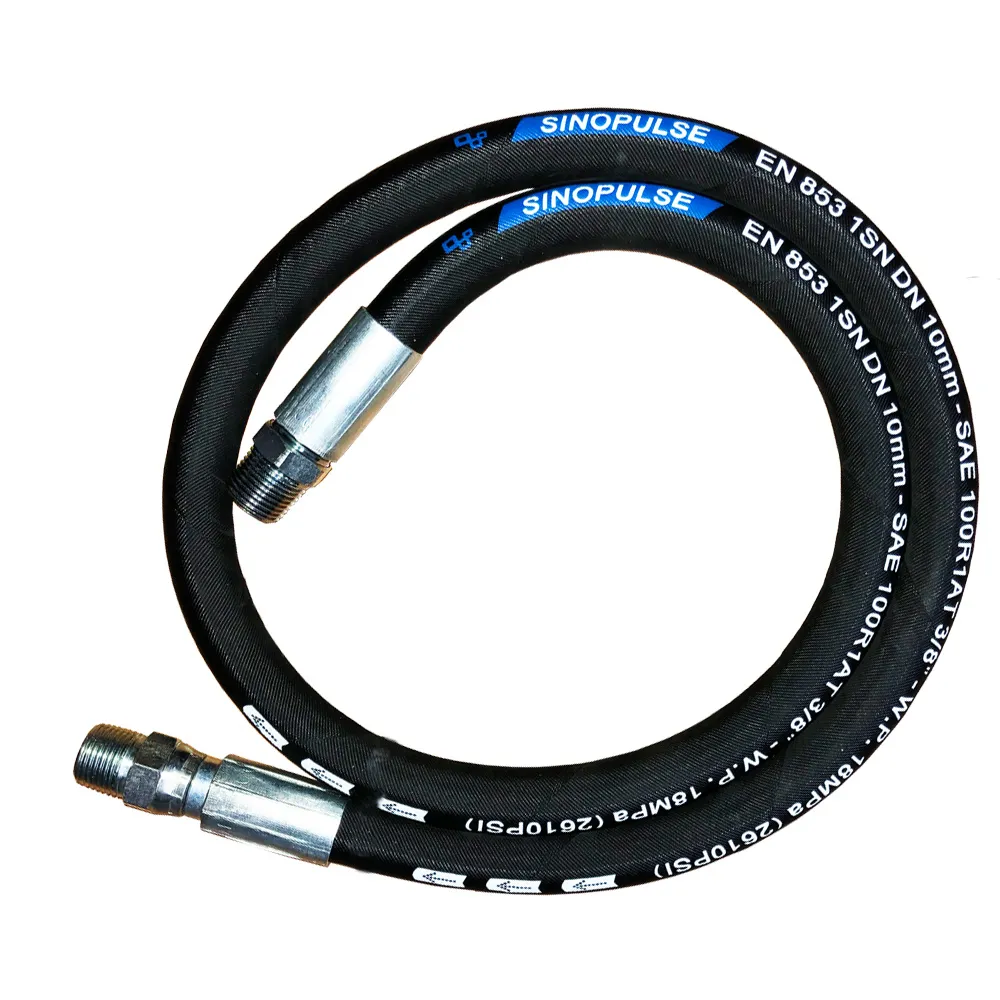
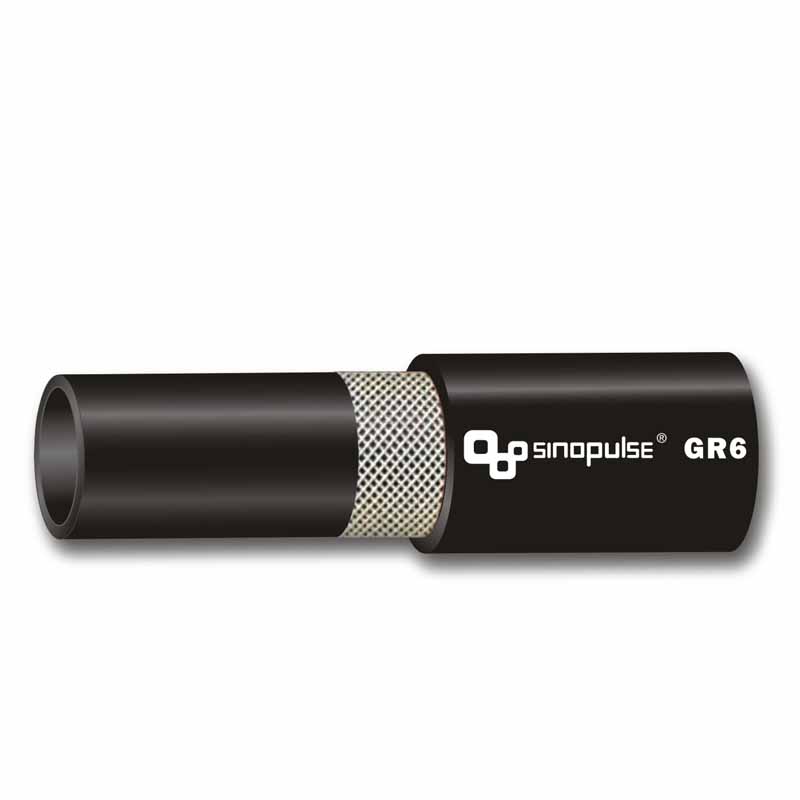
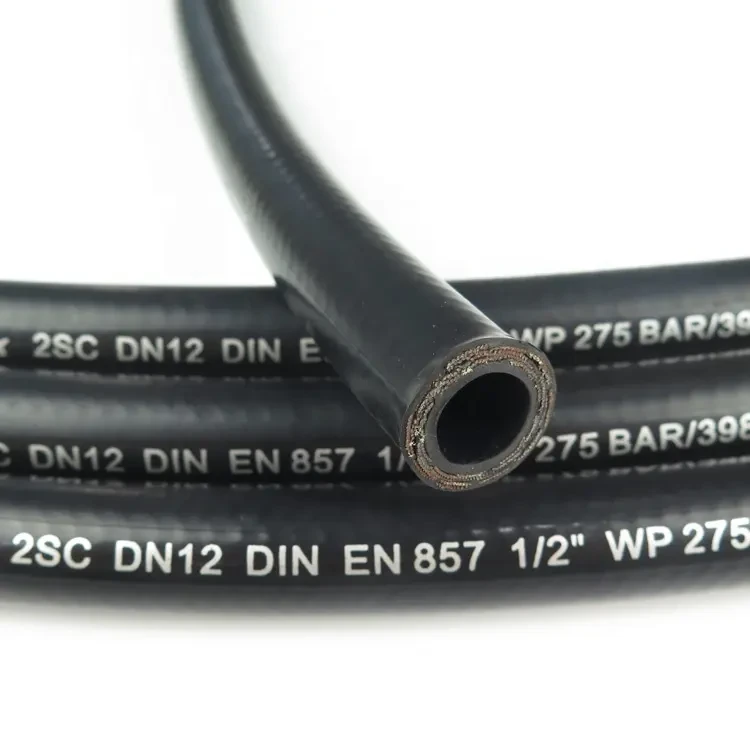
Hydraulic rubber hose , a staple in heavy machinery, exemplifies its strength: reinforced with wire-braided rubber hose layers, they handle pressures up to 6,000 PSI, powering excavators, agricultural tractors, and industrial presses. Other specialized rubber hoses include:
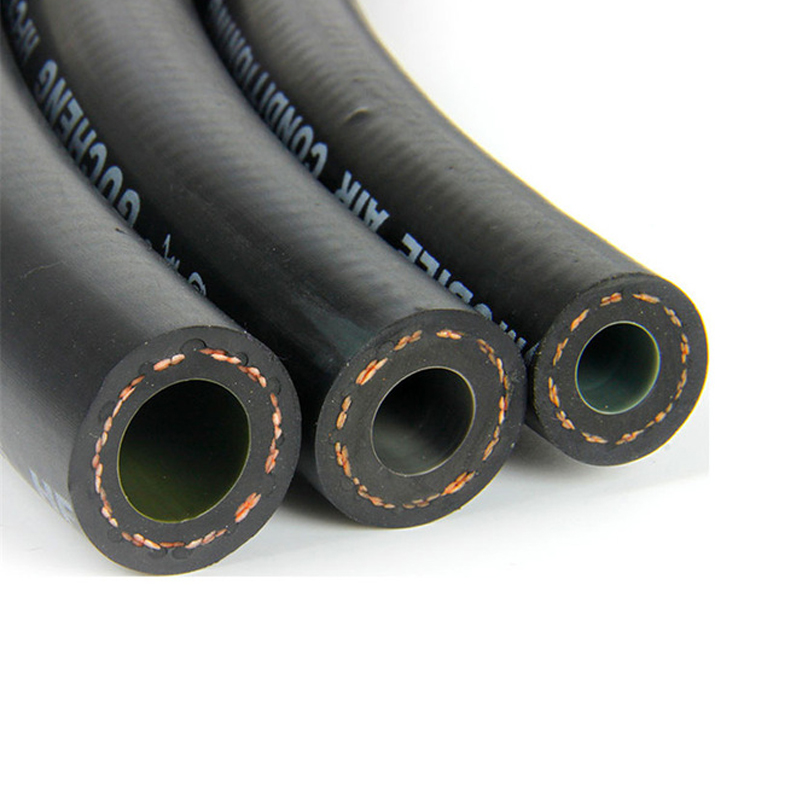
- Chemical rubber hose : Made with EPDM or PTFE-lined synthetic rubber, resisting corrosive fluids like acids and solvents in chemical processing plants.
- Rubber fuel oil hose : Nitrile-based, designed to contain petroleum-based fuels without swelling or degradation, vital for automotive and marine fuel systems.
- Rubber welding hose : Reinforced to withstand high pressures and flame exposure, safely delivering oxygen and acetylene in welding operations.
Rubber hoses shine in durability, withstanding abrasion, UV exposure, and mechanical stress—traits that make them workhorses in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
The choice between them boils down to five critical factors:
- Temperature Range : Silicone dominates extreme highs and lows (-60°C to 200°C), while rubber (EPDM or nitrile) performs best in -40°C to 120°C, with specialized formulations reaching 150°C.
- Chemical Resistance : Rubber (especially nitrile) excels with oils, fuels, and chemicals; silicone resists water, steam, and mild substances but falters with harsh solvents.
-
Pressure Handling
:
Wire braided rubber hoseand hydraulic rubber hose handle 3,000–6,000 PSI, far exceeding silicone’s 100–500 PSI limit.
- Abrasion & Wear : Rubber’s tough outer layers (often reinforced with textile or steel) outlast silicone in rough environments, such as construction sites or mining operations.
- Cost & Application : Silicone, with its food-grade and high-temperature perks, comes at a premium, while rubber offers cost-effective durability for industrial work.
Selecting the right hose starts with asking four key questions:
-
What fluid are you transferring?
For oils, fuels, or chemicals,
chemical rubber hoseor rubber fuel oil hose (nitrile-based) is non-negotiable. For water, steam, or food products, silicone ensures purity.
- What’s the operating temperature? Extreme cold or heat (e.g., bakery ovens, freeze-drying facilities) demands silicone. Moderate ranges (industrial machinery) favor rubber.
- What pressure will the system exert? High-pressure hydraulic systems require a hydraulic rubber hose with a wire braid. Low-pressure applications (ventilation, light transfer) can use silicone.
- What’s the environment like? Abrasive surfaces, UV exposure, or mechanical stress call for rubber’s ruggedness. Clean, controlled environments (pharmacies, kitchens) benefit from silicone’s inertness.
As a leading
Whether you need the high-temperature resilience of silicone or the industrial grit of rubber, we deliver solutions engineered for longevity and safety. Choose SINOPULSE, and let the right hose elevate your operational efficiency—because in fluid transfer, precision matters.
–>